
Ah, how the human mind is a complex and mysterious thing. How can one become so easily entrapped by addiction without awareness? What happens when this addiction destroys not only one’s physical health but also their cognitive functions? It is an unfortunate truth that many do not recognize until it is too late; how you are destroying your peak dopamine levels and brain neuroplasticity with addiction.
It was seemingly coincidental then that I happened upon recent research on this subject, which had gone largely unnoticed in our society. After reading through the findings, I could help but be struck by the stark reality of its implications – namely, if we as individuals continue to partake in self-destructive behavior such as addictions, then we risk damaging our natural ability for growth and development.
For those who may have been unaware of the dangers posed by addiction before now, let me take you on a tour of understanding why exactly these activities have the potential to cause us to harm both mentally and physically. Let us explore how you destroy your peak dopamine levels and brain neuroplasticity with addiction.
What Is Neuroplasticity?
My dear reader, let us explore the notion of neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity is an ever-changing ability of our brain to remodel its neural pathways in response to new experiences or situations. It’s a process whereby neurons are born and adapt their connections to serve us best – it helps us learn, remember, and respond accordingly.

It has become increasingly clear that addiction can profoundly affect our brains’ ability to form these crucial synaptic links.
Addiction Overstimulates Dopamine Receptors
Addictive drugs such as cocaine work by overstimulating dopamine receptors, leading to changes within the brain’s reward system, which cause cravings for more substances and lead to compulsive use disorders. This overexposure leads to the downregulation of dopamine receptors – essentially killing off peak levels of dopamine production – while simultaneously disrupting natural plasticity processes within the brain.
The result?
Our brains become less capable of learning from experience and forming new memories; they cannot keep up with what we ask them to do!
The Link Between Addiction And Neuroplasticity
Addictions can lead to long-term damage to the very essence of how we think and process information.
To understand this better, let us break it down into three key points:
- Addictive substances cause increased activity in neural pathways for pleasure – such as those involving the nucleus accumbens – thus creating dopamine surges when engaging with drugs of abuse.
- As these repetitive behaviors become engrained within our brains over time, they alter the structure and function of our neurons, leading to changes in behavior and cognition that affect overall health and well-being.
- Unfortunately, these changes can be permanent if left unchecked, making a recovery from substance use disorders more complex than ever due to their profound influence on neurological functioning.

In short, addiction impairs our brain’s plasticity by altering neuronal structures through repeated exposure to drugs of abuse or other forms of addictive behavior. Consequently, this increases susceptibility towards developing mental illnesses and can create a downward spiral that further exacerbates problems like depression or anxiety.
Now let us move onward and see just how dopamine affects the brain…
What Is Dopamine And How Does It Affect The Brain?
Dopamine is like the golden key to our brains- unlocking cognitive functions and providing us with rewarding effects. It’s no wonder we become so addicted to its alluring presence! But what exactly is dopamine, and how does it affect neuroplasticity?
In short, dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate various cognitive processes such as motivation, reward systems, and addictive behaviors. It works by binding to receptors on neurons within the brain and triggering chemical reactions that allow for better communication between nerve cells. This ultimately results in elevated pleasure or reward when certain activities are performed. Consequently, this creates a powerful incentive to continue doing those activities and can lead to addiction if not appropriately managed.
The release of dopamine also plays a significant role in strengthening neural pathways in the brain through neuroplasticity – meaning it changes the structure of our brains when we do something pleasurable over time. This means that any activity which triggers the release of dopamine has the potential to rewire our brains; from video games to drugs, both affect dopamine levels and, thus, our overall mental health.
How Does Addiction Negatively Impact Dopamine Levels?
The brain is like a magical kingdom, where the alchemy of dopamine creates an elixir of joy. But addiction acts as a thief in the night, stealing away such pleasure and leaving only destruction and despair behind.
Addiction negatively impacts peak dopamine levels by hijacking the reward pathways it needs to function correctly.

According to National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) research, pathological gambling has been linked with lower-than-average dopamine levels. This low level of natural dopamine can lead to Reward Deficiency Syndrome – meaning that individuals cannot feel pleasure without external substances or activities. As this cycle continues, the brain loses its ability for neuroplasticity – which usually helps us learn new skills and build stronger connections between neurons.
Without proper treatment, these effects will become more pronounced until our brains succumb to their fate: no longer able to find solace from within but always needing something outside for comfort – slowly destroying themselves piece by piece.
The Causes Of Addiction
The causes of addiction are a black hole swallowing up the lives and potential of its victims. From compulsive gambling to behavioral addictions such as internet usage disorder, there is no end to the list of ways people can fall prey to this insidious affliction. Understanding what leads someone down the path of cognitive decline and potentially ruinous consequences is essential before it’s too late.
First, let us look at how one might become addicted in the first place:
1. Biological Causes:
Scientists have identified specific genetic traits that predispose individuals toward addictive behavior. Chronic drug use can sometimes alter brain chemistry to create an environment conducive to further addiction.
2. Psychological Causes:
Low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety are part of a psychological profile that may lead someone into indulging in activities they know will not bring them true happiness or contentment – but provide a reprieve from their mental state.
3. Social Factors:
Friendships with those who partake in addictive activities should also be seen as red flags for those vulnerable to succumbing; peer pressure is compelling, after all!
It is clear then that addiction stems from internal and external sources; recognizing these signs could save a person from falling into such behaviors and hopefully prevent any long-term damage from compulsive habits.
Before we move on, however, allow me to emphasize once more how vital it is for everyone – young or old alike – to take proactive steps against becoming enslaved by their desires and emotions lest they find themselves unable to break free again without help.
With these facts laid bare before us, our next step must be understanding addiction’s devastating effects on brain neuroplasticity… …and developing strategies to help those affected by its damaging effects rebuild their lives.
The Effects Of Addiction On Brain Neuroplasticity
Addiction has a devastating effect on one’s brain neuroplasticity as if it were an insidious fog slowly consuming the very essence of that which makes us human. The destruction is multifaceted and complex, akin to a many-headed hydra: animal studies have shown executive function impairment, long-term depression, and dopamine levels plummeting into oblivion.

To paint this bleak picture in more vivid detail:
- addiction can compromise our ability to make decisions;
- those afflicted may experience high levels of anxiety and low moods for extended periods;
- cravings become all-consuming and compel individuals towards relapse;
- pleasure receptors throughout the brain are dulled as dopamine production decreases with overuse.
It is clear then that addiction can ruin both body and mind. Understanding how best to treat sufferers is paramount – lest we stand idly while they fall further into a deep abyss of despair.
Possible Treatments For Addiction
According to a study published in the Indian Journal of Psychiatry, an estimated 20 million Indians suffer from substance use disorder. The study also reported that alcohol and opioids were the most common substances abused in India.
Fortunately, there are treatments available for those struggling with these issues.
When it comes to treating addiction, one of the most beneficial forms of treatment is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). This therapy helps individuals recognize problematic behaviors and develop healthier ones to prevent relapse.
Other treatments include support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous or Narcotics Anonymous, medications like buprenorphine or naltrexone that reduce cravings and manage withdrawal symptoms, and psychotherapy focusing on understanding underlying mental health conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and major depression.
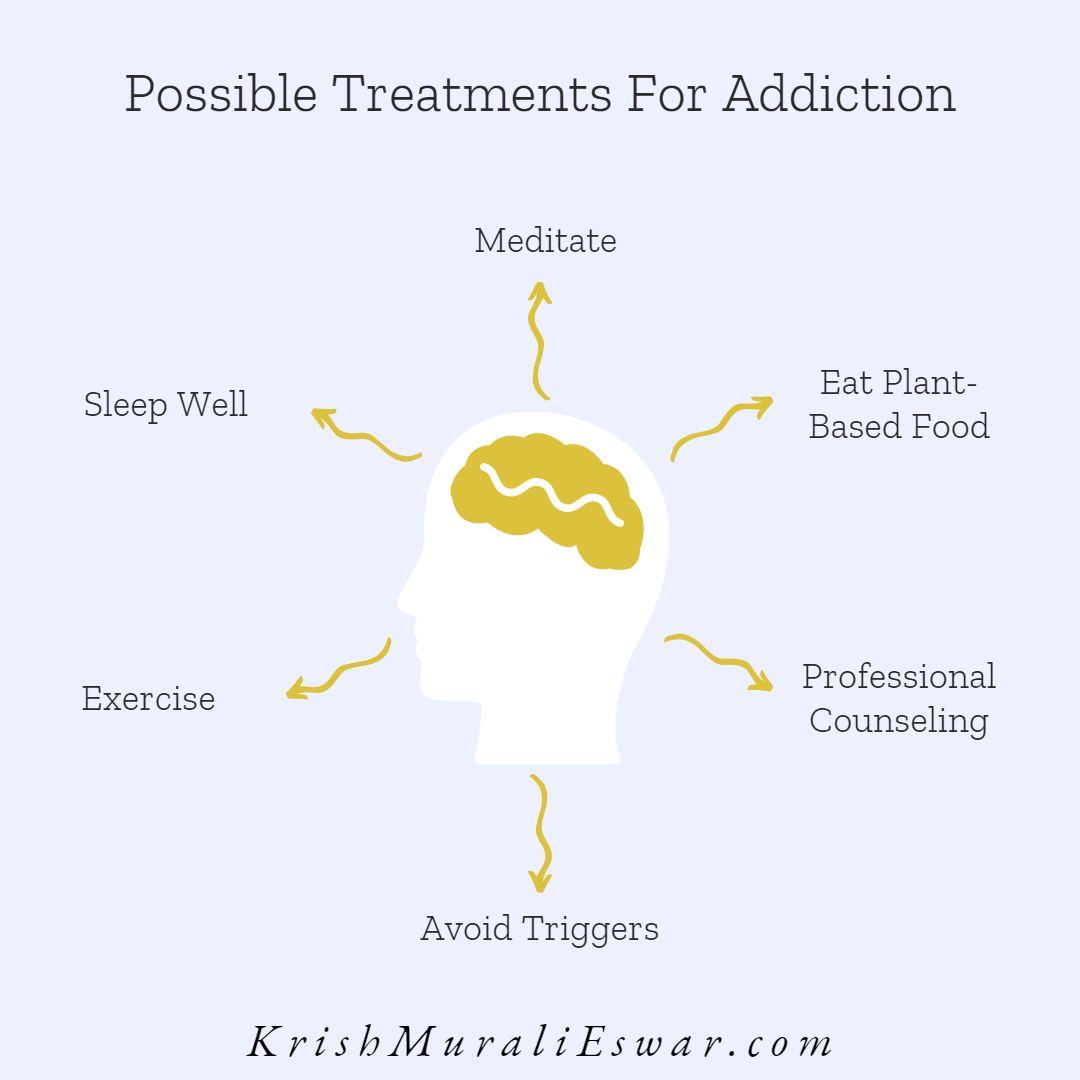
Some lifestyle changes may help alleviate the effects of addiction. These include:
- engaging in regular exercise,
- creating healthy habits around sleeping patterns,
- practicing meditation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or yoga,
- eating nutritious foods,
- avoiding triggers associated with past substance abuse experiences, and
- seeking professional counseling when necessary.
These activities can be incredibly beneficial in reducing stress levels and keeping addicts from relapsing into old destructive habits.
The Role Of Stress In Addiction
Like a thief in the night, stress has slowly stolen away dopamine levels and neuroplasticity from our brains.
When long-term depression sets in, individuals often rely on nonhabitual rewards such as drugs or alcohol for comfort.
This habit formation can be challenging to break due to the altered brain chemistry and environment created by addiction. Over time, these activities take precedence over all other aspects of life and significantly reduce peak dopamine levels and neural plasticity. Furthermore, without proper clinical intervention, it becomes increasingly more difficult to regain control over addictive behavior patterns.
The power of genetics should not be overlooked when discussing addiction either; research continues to indicate that those with family members who suffer from stress and substance abuse are much more likely to end up down the same road themselves. Combining environmental factors such as poverty or mental illness alongside genetic predispositions can create an uphill battle for anyone trying to overcome their addictions.
The Role Of Genetics In Addiction
The role of genetics in addiction is an intriguing conundrum. It often appears that some people are born with a predisposition to substance abuse, while others may be able to resist the lure of drugs and alcohol more quickly.
In truth, much as with any other topic involving human behavior, it is likely that both nature and nurture play their respective roles when considering why someone might develop an addiction.
The nucleus accumbens, which plays a critical role in reward-seeking behaviors and expression of dopamine release, can certainly have its functionality impacted by genetic variants; these variations could mean the difference between an individual being tempted by substances or having the natural ability to exert control over cravings.
Drugs can also alter gene expression through epigenetic modifications: changes made on top of existing DNA sequences without altering them directly. This means that even if someone isn’t predisposed genetically towards substance use disorder, long-term exposure to certain substances can cause changes in gene expression which increase vulnerability for addiction – so it’s essential to understand both environmental influences as well as family history when assessing risk factors for developing addictions.
Understanding how genetics interacts with the environment will help us gain further insight into addiction’s complex mechanisms.
The Impact Of Social Environment On Addiction
It is well-known that addiction, not just genetics, can be shaped by one’s social environment. This has been confirmed through numerous clinical studies which have revealed the behavioral effects of social and environmental factors on those suffering from substance abuse issues. These external influences cannot be overstated; they play an essential role in how much striatal dopamine release and subsequent peak dopamine levels are experienced when engaging in addictive behaviors.
The evidence points to social conditions as significant contributors to patterns of addiction. It would therefore make sense for us to consider our environments before we fall victim to any habit or behavior that could become problematic. To break this cycle of destructive addictions, it might be wise to consider how our daily interactions may influence our choices and decision-making processes – even if only subconsciously!
How To Identify Signs Of Addiction
The signs of addiction are all too clear but frequently ignored. One must be vigilant to identify them in others or even themselves.
It’s essential to pay attention to behaviors that could lead one down the path of addiction, such as:
- excessive drinking,
- smoking,
- gambling,
- lack of interest in social interaction,
- oversleep or sleep deprivation,
- emotional instability,
- mood swings,
- taking cognitive enhancers without medical supervision, or
- engaging in risky sexual activity.
Any changes in mindset or behavior should be taken seriously; if someone has suddenly begun exhibiting these behaviors, it might indicate that addiction has already taken root. If you think someone close to you may have a problem, talking openly about their situation would be an appropriate first step toward helping them get back on track.
Strategies To Overcome Addiction
It is as though addiction to substances has a vice-like grip on our brains, its tentacles reaching deep into the nucleus accumbens and clinging with fierce tenacity. Overcoming this insidious force requires courage, determination, and resilience, but it can be done.
Recognize that addiction is real: statistical significance proves its existence beyond doubt. We cannot deny that if left unchecked, addiction will destroy dopamine levels and neuroplasticity in the brain. Therefore, we must take action to reduce dependence on these substances – for our good!
We should begin by replacing bad habits with positive ones: instead of alcohol or drugs, find healthier activities that bring joy and satisfaction. Exercise releases endorphins and helps us stay focused on other goals. Find friends who support your path away from addiction rather than encourage the use of substances. And remember that breaking any habit takes time – so don’t give up when progress seems slow!
By committing to strategies designed to overcome addiction, we retake control of our lives, bringing freedom and immense satisfaction.
The Benefits Of Reducing Dependence On Substances
On the one hand, addiction can take a heavy toll on our brains. It has been shown to decrease dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens, which affects our ability to experience pleasure and reinforces compulsive behaviors. On the flip side, reducing dependence on substances offers many benefits.
By taking steps towards recovery, we are actively working to improve our brain’s neuroplasticity and restore its peak performance capabilities. Doing so will help us make healthier choices and reduce cravings for any addictive substance we may have had trouble with. Furthermore, as we become more mindful of how these things affect us mentally and physically, it becomes easier to develop lasting habits that support better mental health outcomes.
The journey from addiction is not easy, but by focusing on self-care and understanding our triggers, we can build healthy habits that promote improved neuroplasticity.
How To Build Healthy Habits To Improve Neuroplasticity
We must look into ways to promote healthy habit formation to repair the damage caused by addiction to improve neuroplasticity.
As much as we might wish for a quick fix or some miraculous cure, there is no easy road to restoring peak dopamine levels and brain plasticity. We must work by learning proper habits that safely cultivate these aspects.
Yoga or meditation can help relax your mind and reconnect you with your inner self.
Regular exercise and enough sleep are also necessary to create a well-balanced lifestyle.
Additionally, incorporating routine behavior changes should become second nature over time – such as consuming healthier snacks rather than processed foods laden with sugar and fat.
It requires dedication and commitment to make lasting changes that improve our physical health and mental well-being; however, if done correctly, the rewards will be immense. By following these guidelines regularly, you’ll find yourself on track toward reclaiming those lost dopamine levels while increasing your capacity for resilience and creativity.
The Long-Term Benefits Of Reducing Addiction
Ah, the long-term benefits of reducing addiction – what a tantalizing prospect! To think that merely by curbing our cravings and habits, we can reap the rewards for years. It’s truly an astonishing thought, one that deserves careful consideration.
The truth is when it comes to our peak dopamine levels and brain neuroplasticity; there are few better ways of preserving them than minimizing addictions. The more we give in to temptations and engage in unhealthy behavior, the more significant damage we do to ourselves in the long run. Not only does addiction tend to reduce cognitive functions like concentration and memory recall, but it also tends to disrupt key processes essential for proper neural development – something that may not be immediately obvious but which could have far-reaching consequences later on down the line.
It’s clear then that breaking free from addictive cycles should be seen as an investment with guaranteed returns: improved mental health and increased resilience against future problems. All this shows how important it is to stay vigilant over our vices and strive towards healthier living standards – because at stake here is nothing less than the fabric of our mindscape!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Long-Term Physical Effects Of Addiction?
1. Inertia: Addiction can cause a person to become increasingly lethargic, with reduced motivation and energy for day-to-day tasks.
2. Deterioration of Health: Chronic substance abuse can lead to weakened immune systems, organ damage, and an increased risk of developing various illnesses or diseases.
3. Loss of Memory: Prolonged addiction can harm memory; research suggests that it may even cause dementia in some cases.
4. Cognitive Impairment: Addiction dulls the senses, leading to slowed reflexes and impaired judgment, preventing one from making sound decisions.
5. Social Isolation: Substance abusers tend to distance themselves from family and friends, alienating them from those closest to them.
6. Financial Problems: Addiction is often accompanied by financial difficulties due to the high cost of obtaining drugs or alcohol and the associated lifestyle changes that come with it, such as quitting jobs or selling possessions for money.
How Can I Improve My Dopamine Levels Without Using Drugs Or Alcohol?
- Eat a Plant-Based Diet: Eating a healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes helps boost dopamine levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Exercising releases endorphins and improves blood flow to the brain, increasing dopamine production.
- Get Enough Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for maintaining healthy dopamine levels; aim for at least 7-8 hours each night.
- Practice Kundalini Meditation: This meditation focuses on breathwork to help clear the mind and reduce stress levels. It can also help raise dopamine levels naturally over time.
- Listen To Music: Listening to music can positively affect serotonin and dopamine levels in the brain, providing an overall sense of well-being and relaxation.
- Take Supplements: Natural supplements can help increase dopamine naturally without resorting to drugs or alcohol.
- Try Yoga: Yoga combines physical exercise with breathing techniques and meditation which all help to release tension in the body while boosting both serotonin and dopamine production in the brain.
Summary: Reclaiming Mental Balance and Well-Being with Co-Occurring Addiction and Mental Health Issues
We have seen that addiction can be a formidable foe, wreaking havoc on our minds and bodies. Taking preventative and restorative measures is essential to ensure we are not destroying our peak dopamine levels and brain neuroplasticity with such afflictions.
For example, I recently met a gentleman who was addicted to alcohol for years. He had sought professionals’ help to help him recover his lost mental health and regain control over his substance use. Through cognitive behavioral therapy coupled with simplified kundalini meditation taught in our Vethathiri SKY Yoga center, he could reduce his cravings, break down any barriers preventing him from seeking recovery, and ultimately make strides toward living an addiction-free life.
The truth remains: if we work diligently at prevention through lifestyle changes, education about the risks associated with addictive substances or behaviors, and early intervention when necessary, we can enjoy healthy lives free of addiction’s destructive path.
Don’t let addiction leave you feeling “down” – take control and reclaim balance!
For more tips on how to beat addiction and mental health issues, subscribe and comment below!
Be Blessed by the Divine!
Krish Murali Eswar.
Leave a Reply